Shanghai and Surrounding Areas: An In-depth Look at the Economic and Cultural Powerhouse
⏱ 2025-05-04 08:28 🔖 上海品茶工作室
📢0℃
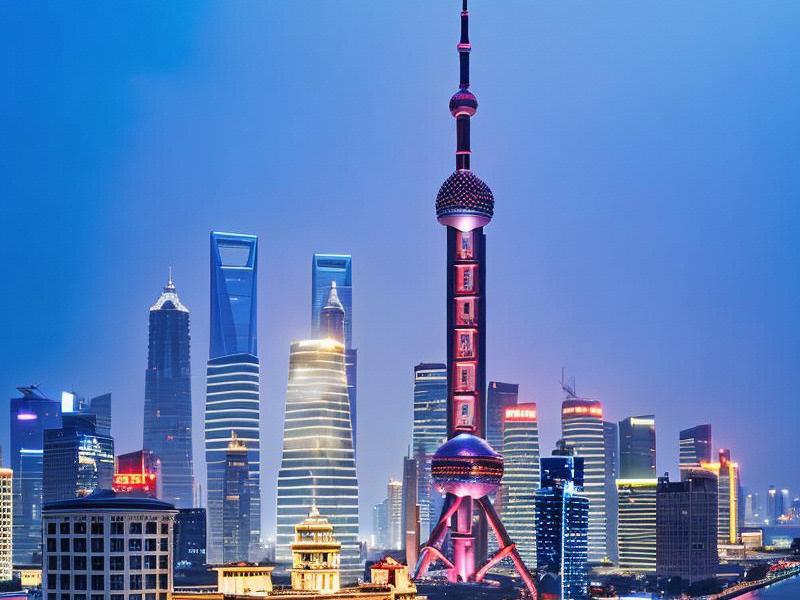

Shanghai, often referred to as the "Pearl of the Orient," stands as a beacon of modernity and progress in China. As the largest city in the country, Shanghai is not only a global financial hub but also a melting pot of cultures, history, and innovation. However, the story of Shanghai's prominence is not confined to the city itself; its surrounding areas, including the Yangtze River Delta region, play a crucial role in shaping its economic and cultural landscape.
Economic Powerhouse
Shanghai's economic prowess is well-documented, with its skyline dominated by some of the tallest skyscrapers in the world, such as the iconic Oriental Pearl Tower and the Shanghai Tower. The city is home to the Shanghai Stock Exchange, one of the largest stock exchanges globally, and is a major center for international trade, finance, and commerce.
The surrounding areas, collectively known as the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region, are equally significant. This region, which includes cities like Suzhou, Hangzhou, and Nanjing, is often referred to as the "engine" of China's economy. The YRD contributes over 20% of China's GDP and is a hub for high-tech industries, manufacturing, and logistics.
One of the key factors driving the economic success of Shanghai and the YRD is the region's strategic location. Situated at the mouth of the Yangtze River, Shanghai serves as a gateway to the vast inland regions of China. The region's extensive network of highways, railways, and waterways facilitates the efficient movement of goods and people, making it a critical node in global supply chains.
Cultural Heritage
爱上海论坛 Beyond its economic achievements, Shanghai and its surrounding areas are rich in cultural heritage. Shanghai, with its unique blend of Eastern and Western influences, offers a fascinating glimpse into China's history and modernity. The Bund, a historic waterfront area, showcases the city's colonial past with its array of Art Deco buildings and European-style architecture. In contrast, the Yu Garden, a classical Chinese garden, reflects the traditional aesthetics of ancient China.
The surrounding areas are no less culturally significant. Suzhou, often referred to as the "Venice of the East," is renowned for its classical gardens, silk production, and traditional Chinese architecture. The city's gardens, such as the Humble Administrator's Garden and the Master of the Nets Garden, are UNESCO World Heritage Sites and attract visitors from around the globe.
Hangzhou, the capital of Zhejiang Province, is famous for its breathtaking West Lake, a UNESCO World Heritage Site that has inspired poets and artists for centuries. The city is also a center for silk production and tea culture, with its Longjing (Dragon Well) tea being highly prized.
Urbanization and Infrastructure
The rapid urbanization of Shanghai and its surrounding areas has been nothing short of remarkable. Over the past few decades, the region has witnessed a massive influx of people, leading to the development of sprawling suburbs and satellite cities. This urban sprawl has been supported by significant investments in infrastructure, including high-speed rail networks, modern airports, and advanced public transportation systems.
The Shanghai Maglev Train, the world's first commercial high-speed magnetic levitation train, is a testament to the region's commitment to innovation and connectivity. Connecting Shanghai to the neighboring city of Pudong, the Maglev train offers a glimpse into the future of transportation.
新夜上海论坛
The surrounding areas have also seen substantial infrastructure development. The Hangzhou Bay Bridge, one of the longest cross-sea bridges in the world, connects Shanghai and Ningbo, facilitating the movement of goods and people between the two cities. Similarly, the Suzhou Industrial Park, a joint venture between the governments of China and Singapore, is a model of modern urban planning and industrial development.
Environmental Challenges
While the economic and cultural achievements of Shanghai and its surrounding areas are impressive, they come with significant environmental challenges. Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to issues such as air pollution, water contamination, and deforestation. The region's heavy reliance on coal for energy production has contributed to poor air quality, prompting the government to implement stricter environmental regulations.
Efforts to address these challenges are underway. Shanghai has launched initiatives to promote green energy, improve waste management, and enhance public transportation. The city's goal is to become a global leader in sustainable urban development. Similarly, the surrounding areas are investing in renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar power, to reduce their carbon footprint.
Future Prospects
爱上海419论坛 The future of Shanghai and its surrounding areas looks promising, with continued economic growth and cultural development. The Chinese government has identified the Yangtze River Delta region as a key area for innovation and high-quality development. Initiatives such as the Integration of the Yangtze River Delta aim to foster greater regional cooperation and coordination, enhancing the overall competitiveness of the area.
Technological advancements are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the region. Shanghai's status as a global technology hub is being reinforced by the establishment of innovation clusters, such as the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park and the ShanghaiTech University. These initiatives are attracting top talent and fostering research and development in fields such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and green technology.
Culturally, the region is poised to become an even more significant global cultural hub. Shanghai's role as a center for art, fashion, and design is growing, with international exhibitions, fashion shows, and cultural festivals attracting visitors from around the world. The surrounding areas are also investing in cultural preservation and promotion, ensuring that their rich heritage is passed on to future generations.
Conclusion
Shanghai and its surrounding areas represent a unique blend of economic dynamism, cultural richness, and rapid urbanization. As the economic engine of China, the Yangtze River Delta region continues to drive the country's growth and development. At the same time, the region's commitment to sustainability and cultural preservation ensures that its legacy will endure.
The story of Shanghai and its surrounding areas is one of resilience, innovation, and transformation. As the world watches, this dynamic region continues to shape the future of China and the global community. Whether through its towering skyscrapers, historic gardens, or cutting-edge technology, Shanghai and its surrounding areas stand as a testament to the boundless potential of human ingenuity and determination.
Shanghai 2040: Where Futurism and Heritage Collide in China's Global MegacityShanghai 2040: How China's Global City Is Reinventing Urban LivingThe Phoenix of the East: How Shanghai is Reinventing Global Cultural InfluenceShanghai's Green Transformation: Pioneering Sustainable Urban Development in the 21st Century【摩登密码】从月份牌到元宇宙:上海女性审美百年流变录Shanghai's Vibrant Lifestyle, from Historical Pedigree to a Global Metropolis【特别调查】"共饮一江水:长三角生态绿色一体化发展示范区三年成效报告"【摩登密码】从石库门到元宇宙:上海女性的百年形象革命Shanghai’s Digital Elegance: Where Tradition Meets Tomorrow’s Frontier in BeautyShanghai's Nightlife Evolution: How Luxury Entertainment Clubs Are Redefining Urban Social Culture
海派烟火眉:上海美女的市井诗行与精神注脚《霓虹深处:南京东路百年商业街的进化论》《百乐门到元宇宙:上海娱乐会所进化论》霓虹与檀香:上海高端会所三十年文化流变"四段式模板
7. 历史参考:前两篇分别以"感官革命"和"时空折叠"为切入点,本次需创新视角
8. 时效元素:当前为2025年,可融入AI、元宇宙等现代科技元素
9. 价值导向:展现独立、智慧的当代上海女性形象,规避物化倾向
以下是符合要求的深度特稿:《梧桐树下的方程式:95后女科学家与旗袍实验室的双城记》《石库门密码:上海里弄建筑的时空折叠》《石库门里的时光标本》《梧桐树下的城市镜像》梧桐区镜像:上海女性的空间叙事与身份建构
空间修辞,身体政治,时尚语法,记忆拓扑,社群算法